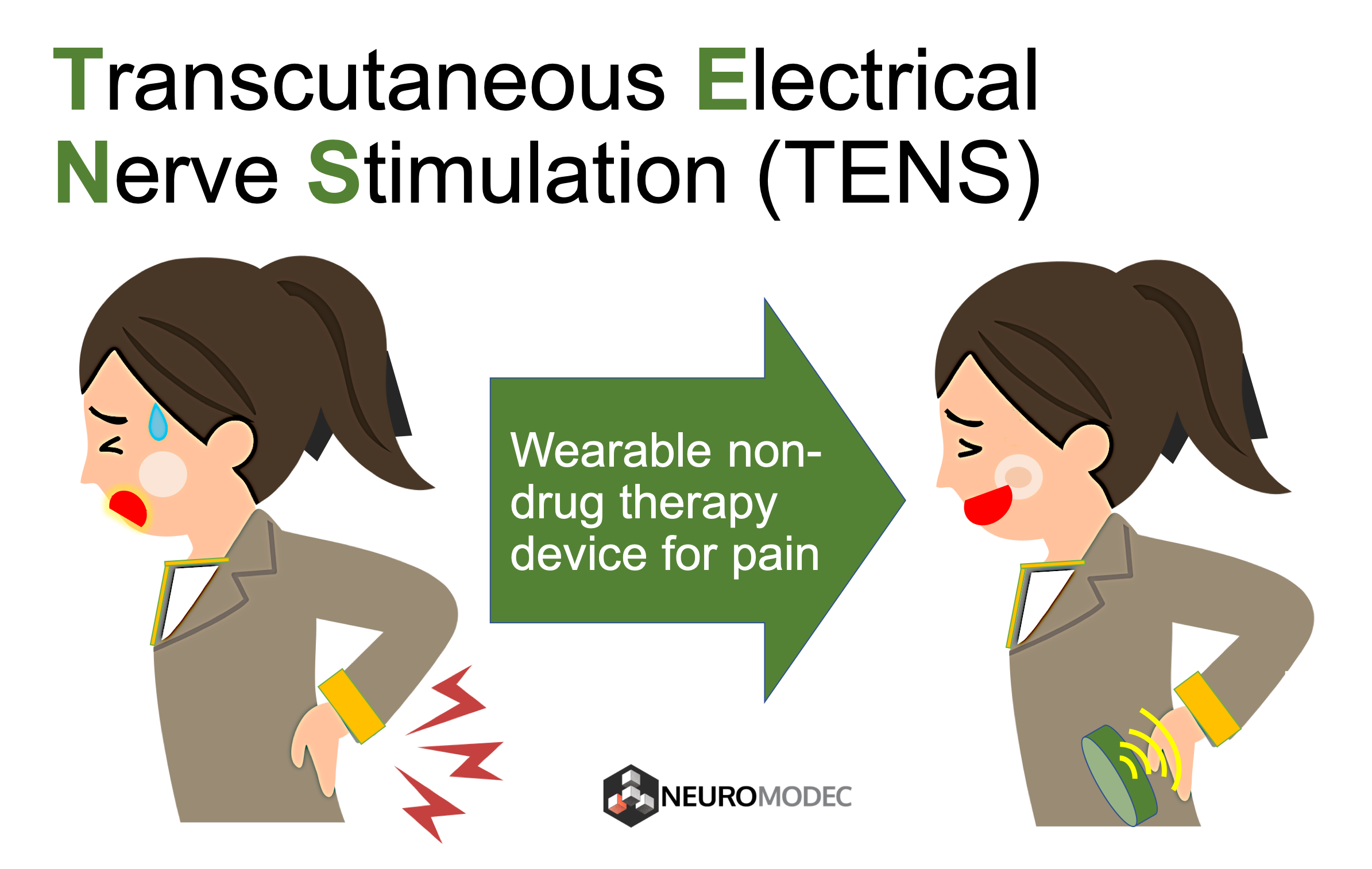
Bilateral Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Improves Upper Limb Motor Recovery in Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial
$ 21.50
-
By A Mystery Man Writer
-
-
5(272)

Product Description

Trigeminal or peripheral nerve stimulation improves functional outcomes of nerve recovery in a rodent forelimb gap repair model - Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery

Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) Alleviates Brain Ischemic Injury by Regulating Neuronal Oxidative Stress, Pyroptosis, and Mitophagy

PDF) Abstract P218: Effects of Bilateral Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Combined With Task-Oriented Training on the Recovery of Upper Limb Motor Impairment in People With Chronic Stroke

Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) Alleviates Brain Ischemic Injury by Regulating Neuronal Oxidative Stress, Pyroptosis, and Mitophagy
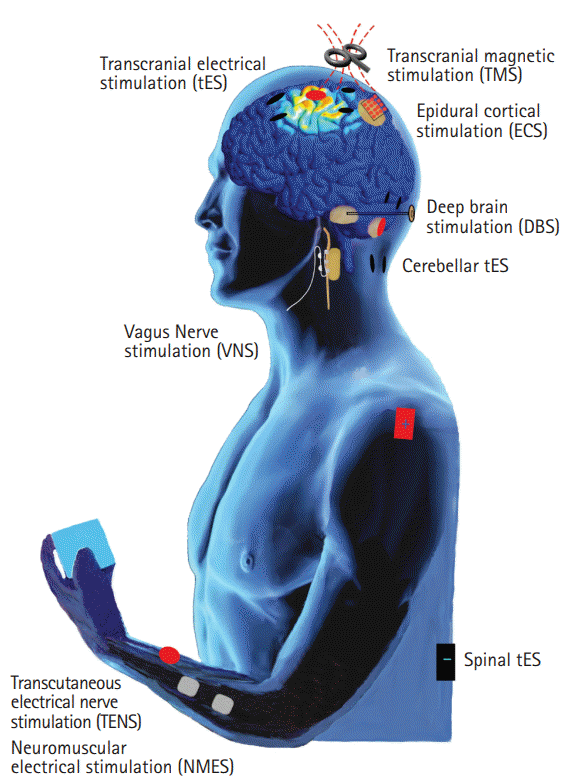
Journal of Stroke

Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation improves walking capacity and reduces spasticity in stroke survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis - Patrick WH Kwong, Gabriel YF Ng, Raymond CK Chung, Shamay SM Ng, 2018

Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation improves walking capacity and reduces spasticity in stroke survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis - Patrick WH Kwong, Gabriel YF Ng, Raymond CK Chung, Shamay SM Ng, 2018
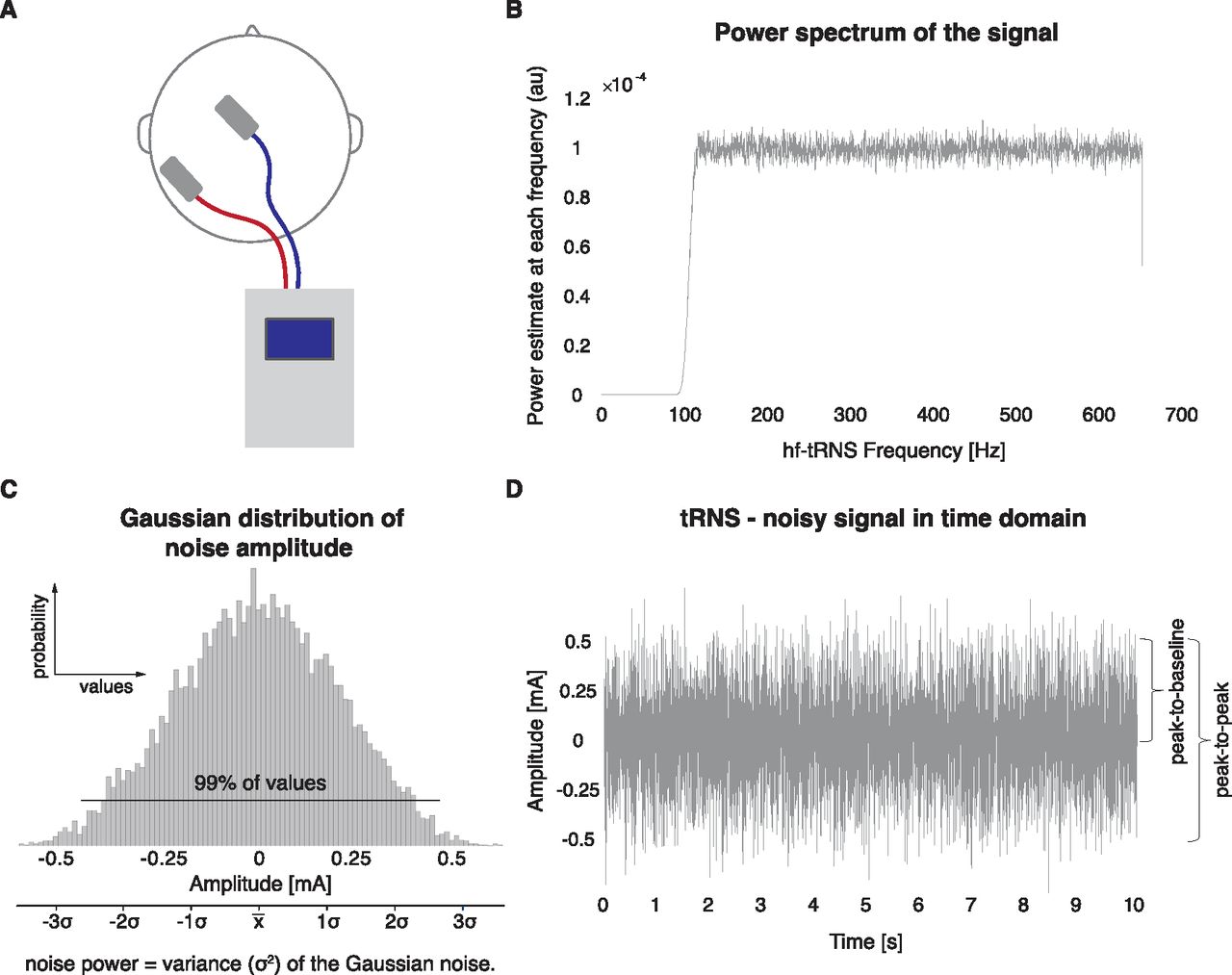
Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation Modulates Neural Processing of Sensory and Motor Circuits, from Potential Cellular Mechanisms to Behavior: A Scoping Review

Transcutaneous Spinal Cord Stimulation to Reduce Phantom Limb Pain in People with a Transtibial Amputation

Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Combined With Task-Related Training Improves Lower Limb Functions in Subjects With Chronic Stroke

Rehabilitation of Motor Function after Stroke: A Multiple Systematic Review Focused on Techniques to Stimulate Upper Extremity Recovery. - Abstract - Europe PMC
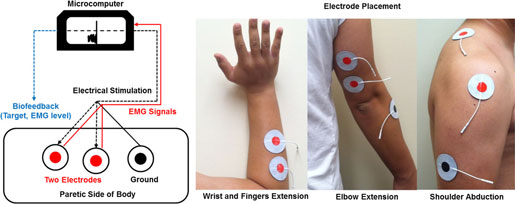
13. Regaining Use of the Upper Extremity
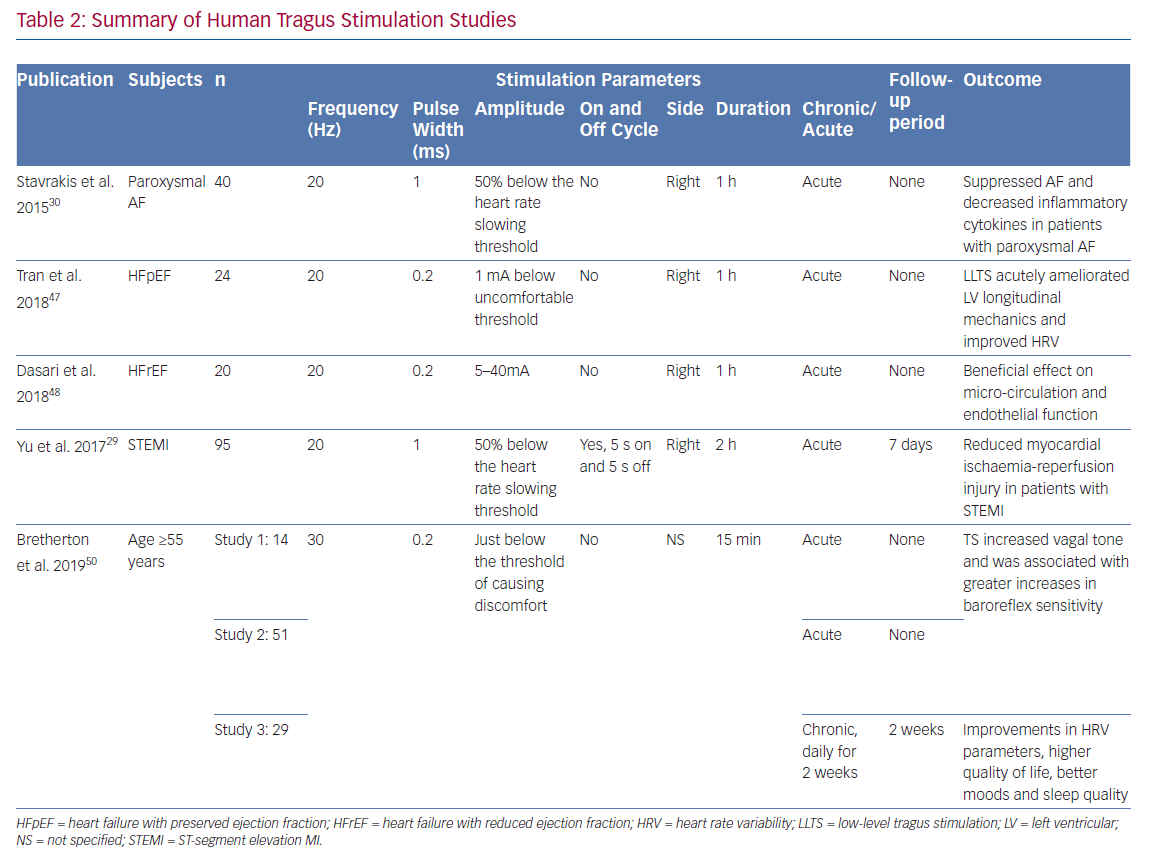
Non-invasive Low-level Tragus Stimulation

STIWELL med4 - Med-El

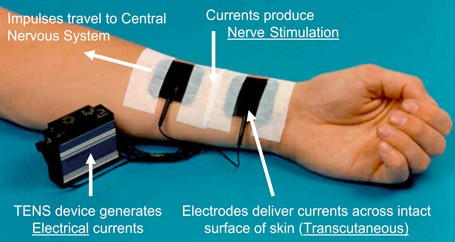
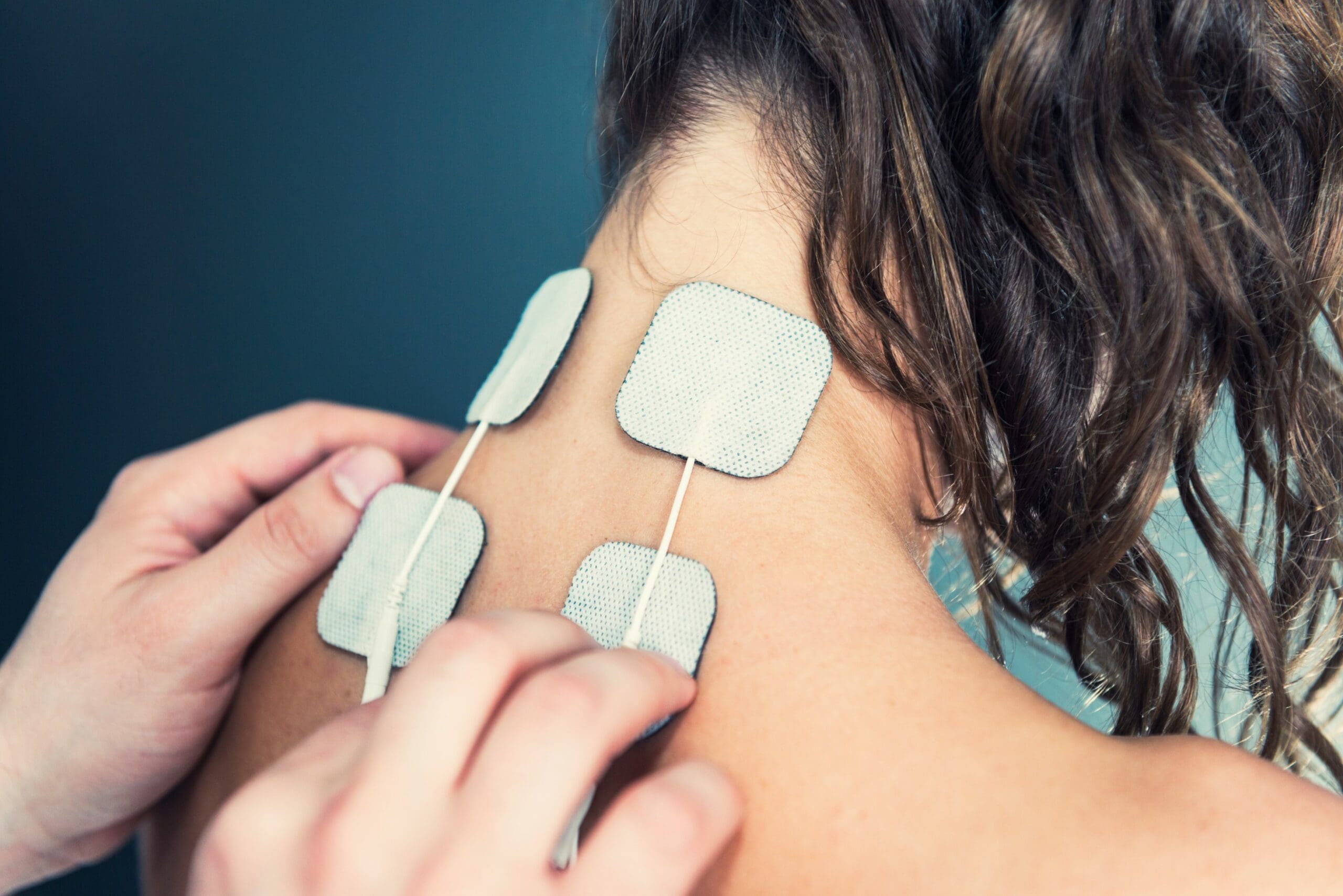
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/186807776-56a6e1835f9b58b7d0e53995.jpg)











